Ancient Egyptian Culture, History and Mythology, Mythology, Mythology and Culture, Mythology and Healing, Mythology and History
The Dark Myth of the ‘Bloody Eye’: Set, Horus, and the Elemental Powers
Introduction to the ‘Bloody Eye’ Myth
The myth of the ‘Bloody Eye’ is deeply entrenched in ancient Egyptian lore, serving as a focal point for the complex relationships among the deities in this rich pantheon. At the heart of this tale lies the fierce rivalry between Set, the god of chaos and disorder, and Horus, the god of the sky and kingship. This conflict encapsulates the broader themes of duality and balance that dominate Egyptian mythology. The ‘Bloody Eye’ myth specifically refers to the legendary battle over the rightful ownership of the throne of Osiris, where the narrative unfolds with both tragic and poetic elements.
The origins of the ‘Bloody Eye’ story can be traced back to the Osiris myth, wherein Set murders his brother Osiris to usurp his power. This act of fratricide not only establishes Set as a symbol of destruction but also sets in motion a series of events that lead to an epic struggle for supremacy. Horus, the son of Osiris, embarks on a quest for vengeance and justice, intending to reclaim his father’s throne. Throughout the myth, the symbolism of the eye plays a crucial role, as it represents not only sight and perception but also the intricate dynamics of power and retribution.
As the battle progresses, it is said that Set inflicts damage upon Horus, including the infamous injury to Horus’s eye. This ‘Bloody Eye’ thus transforms into a profound symbol within the myth, denoting both physical suffering and deeper spiritual significance. The narrative weaves together themes of loss, vengeance, and ultimately, the restoration of order, encapsulating the tumultuous relationship between Set and Horus. As we delve deeper into this ancient tale, we will explore the implications of this myth on Egyptian culture and its resonance through history, revealing the layers of meaning beneath this compelling story.
The Characters: Set and Horus
In the rich tapestry of Egyptian mythology, Set and Horus represent two contrasting forces that are pivotal to the understanding of balance within the universe. Set, often depicted with the head of a mythical creature resembling a donkey, is the god associated with chaos, disorder, and violence. He is frequently characterized as a formidable antagonist whose attributes include cunning, ferocity, and a penchant for disruption. As the embodiment of the tumultuous aspects of nature and human behavior, Set is primarily associated with storms, the desert, and the darker elements of existence. His narrative often revolves around battles against his brother Osiris and nephew Horus, highlighting the perpetual struggle between chaos and order.
In stark opposition to Set stands Horus, the falcon-headed god, whose attributes symbolize kingship, order, and protection. Horus is celebrated as the rightful heir to the throne of Egypt, embodying the principles of justice and rightful rule. His association with the sun and the sky, coupled with his role as a divine protector of the pharaohs, underscores the significance of divine kingship within Egyptian culture. The myth of Horus’ conflict with Set is crucial; it not only encapsulates the tumultuous struggle for power but also represents the universal struggle between good and evil. This rivalry, detailed in ancient texts, showcases Horus as the champion of order, reflecting the societal need for structure and governance, contrasting sharply with Set’s unpredictable nature.
The dynamic between Set and Horus illustrates a fundamental duality in Egyptian cosmology. While Set perpetuates disorder, Horus restores balance, and together they signify the constant interplay of opposing forces in the natural world. Their complex interplay offers insight into Egyptian beliefs about morality, governance, and the balance necessary for harmony in both human life and the cosmos.

The Conflict: The Battle for Supremacy
The mythological confrontation between Set and Horus is a profound representation of the power struggle for supremacy over Egypt, encapsulating broader themes of chaos versus order and the cyclical nature of life and death. In ancient Egyptian mythology, Set, the god of chaos, storms, and disorder, embodies the tumultuous forces of nature. His challenger, Horus, symbolizes protection, kingship, and the harmonizing powers of the state. The conflict between these two deities reflects not only their personal vendetta but also the ongoing struggle between disruptive energies and the quest for stability.
The battle for supremacy commenced after the death of Osiris, Set’s brother and the previous ruler of the divine realm. Set’s brutal act of murdering Osiris led to his eventual accession to power, but his reign was marked by disorder and fear. Horus, the son of Osiris and Isis, claimed his rightful place on the throne, thus igniting a series of epic confrontations between the two gods. The nature of their conflict is emblematic of the cyclical aspects of life and death, as Horus sought to avenge his father and restore balance to Egypt by defeating the chaotic force that Set represented.
This ongoing rivalry has deeper implications in society, illustrating the necessity of order to counteract chaos. Horus’s victory and subsequent ascendance to the throne signify not just the triumph of order over chaos, but also the establishment of a legitimate ruling dynasty that aligns with the principles of Ma’at, the ancient Egyptian concept of truth, balance, and cosmic order. Thus, the relentless struggle between Set and Horus narrates the broader themes prevalent in ancient Egyptian mythology, epitomizing the importance of maintaining equilibrium in the universe and continually confronting the tumultuous forces of disorder. The resolution of their conflict reveals the perpetual cycle of life, death, and rebirth, serving as a reminder of the interconnectedness of these elemental powers in shaping Egypt’s mythological landscape.

The Disfigurement: Horus’s Left Eye
In Egyptian mythology, the encounter between the gods Horus and Set is rife with conflict and complexity, exemplified poignantly by the moment when Set dismembers Horus’s left eye. This grievous act surges beyond mere physical disfigurement; it encapsulates themes of duality, struggle, and transformation inherent in the mythos. Set’s violent action can be interpreted as a manifestation of chaos opposing the order that Horus strives to uphold. The loss of the left eye, often associated with the moon, signifies not only a physical mutilation but also an enduring vulnerability within Horus’s identity as a deity of protection and kingship.
The left eye of Horus, known as the “Wedjat,” holds profound significance within the Egyptian cosmology. It is emblematic of healing, wholeness, and divine protection. Consequently, its dismemberment serves as a symbolic representation of loss that transcends the corporeal, affecting Horus’s capabilities to wield power. In many layered interpretations, the eye embodies the notion of sight and perception—qualities associated with rightful sovereignty. Thus, the act of its severance could be viewed as an attempt to undermine Horus’s authority and hinder his capacity to protect and govern.
Additionally, the mythology surrounding the disfigurement feeds into the broader narrative of Horus’s struggle for legitimacy against Set’s chaotic forces. While he suffers a significant loss, the interconnected mythologies suggest that from this disfigurement, a path to eventual restoration and empowerment arises. The eye symbolizes the cyclical nature of life and death, the battles between chaos and order, and, ultimately, the potential for regeneration. This duality is crucial in understanding how Horus possesses the resilience to reclaim his identity amidst the relentless adversities that characterize the tumultuous interactions with Set.

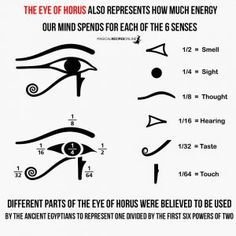
The Six Pieces: Elemental Powers Unleashed
In Egyptian mythology, the eye of Horus is not merely a symbol of sight and protection, but it is dissected into six distinct pieces, each serving as a reservoir of elemental powers. Each segment personifies different natural forces, thereby offering insights into the remarkable connection between the elements and the mythology that surrounds them.
The first piece represents the element of Earth. Known for its grounding properties, this fragment symbolizes stability, nourishment, and life. It signifies the rich fertility of the Nile Delta, which was revered in ancient Egyptian culture as a giver of life. The Earth element reminds us of the intrinsic connection between natural habitats and agricultural prosperity, which was vital for sustaining civilization.
Next comes the piece associated with Water. This segment epitomizes fluidity, adaptability, and transformation. In Egyptian lore, water is often linked to the Nile River, a life source that facilitated trade, agriculture, and transportation. Water also plays a significant role in rebirth, reflecting the cyclical nature of life and death within Egyptian belief systems.
The third piece is tied to Fire. This element represents passion, purification, and destruction, embodying the duality of fire as both a creator and a destroyer. In the context of Horus’s eye, it signifies revelation and enlightenment, illuminating the path to wisdom while also expressing the potential for chaos.
The fourth segment corresponds to Air. This piece symbolizes freedom, communication, and the spiritual realm. In Egyptian mythology, the winds were seen as vehicles for the gods, facilitating the exchange between the heavens and the earth. This element represents the breath of life, emphasizing the importance of both physical and spiritual existence.
In addition, we find the piece that embodies Lightning. This fragment serves as a symbol of sudden transformation, inspiration, and divine intervention. Lightning, in many cultures, is associated with the power of the gods, showcasing the destructive yet often necessary nature of change within life’s cycles.
Lastly, the sixth piece encompasses the element of Time. Although a more abstract concept, it links the cyclical nature of existence. Time in Egyptian mythology is measured by natural rhythms, reminding us of the interconnectedness of the elements in shaping human experience.
Each of these six pieces of Horus’s eye encapsulates unique elemental powers, emphasizing their significance within the broader context of Egyptian mythology. Together, they demonstrate how natural forces intertwine with cultural beliefs, forming an integral part of the fabric of ancient Egyptian life.
Symbolism and Poetics of the ‘Bloody Eye’
The myth of the ‘Bloody Eye’ serves as a profound emblem of the eternal conflict between light and darkness, an archetypal struggle that resonates through various cultural narratives. At its core, this tale reveals deeper truths about existence, encapsulating humanity’s perpetual quest for understanding and enlightenment. The ‘Bloody Eye,’ often associated with the god Horus, symbolizes the protective powers of insight and vision, transcending mere physicality to embody a spiritual journey towards clarity and comprehension.
Within this narrative framework, the bloodshed linked to the eye signifies sacrifice and the inherent pain in the pursuit of knowledge. The eye, representing perception and awakening, is often juxtaposed with shadowy elements that symbolize ignorance and despair. This duality prompts reflection on the human condition, where enlightenment is frequently accompanied by struggle. The tensions between these contrasting forces—darkness and light, ignorance and knowledge—foster a rich tapestry of meaning, offering insights into the complexity of human experiences.
Moreover, the myth draws on elemental powers, establishing a connection to the natural world as well. The ‘Bloody Eye’ can be seen as a metaphor for the turbulent waters of emotion and consciousness, as well as the fiery desire for truth that often fuels the human spirit. Just as spirits navigate the realms of existence, intertwining fate and choice, the myth encourages the exploration of one’s inner chaos. This transformative journey underscores an essential truth: the path to enlightenment may be fraught with trials, yet it is through these experiences that individuals can truly grasp the significance of their own existence.
Ultimately, the symbolic nature of the ‘Bloody Eye’ serves as a mirror reflecting our ongoing struggle to balance the forces of darkness lurking within and the illuminating light of understanding. Through this poetic lens, the myth transcends its historical origins, inviting reflection on universal truths while encouraging individuals to embrace their unique journeys toward wisdom.

Cultural Impact of the ‘Bloody Eye’ Myth
The ‘Bloody Eye’ myth, rooted in ancient Egyptian mythology, continues to wield a significant influence on both historical and modern cultural landscapes. This myth, which centers around the struggles between Set and Horus, has transcended time and geography, serving as a rich narrative source for various forms of storytelling and art. Its impact is evident in literature, visual arts, and cinematic adaptations, showcasing the enduring relevance of its themes and archetypes.
In ancient Egypt, the myth served multiple purposes. It was not only a religious narrative but also a political symbol, as the conflict between Set and Horus reflected the historical struggles for power among pharaohs. This duality has allowed the myth to be interpreted in different contexts over centuries. As a result, many contemporary works draw upon its elements, reimagining the characters and their struggles in new and meaningful ways.
In modern storytelling, the ‘Bloody Eye’ myth has inspired countless adaptations. For instance, it has influenced popular literature, where authors reinterpret the dynamics between Set and Horus, often to explore themes of conflict, revenge, and redemption. Art, too, has been significantly shaped by this myth; contemporary artists incorporate visual motifs associated with the ‘Bloody Eye’ into their work, melding ancient symbolism with current societal issues. Such practices not only preserve the myth but also adapt its message for modern audiences.
The resonance of the ‘Bloody Eye’ myth can also be traced in film and television, where its components are often used to create complex narratives that reflect the human condition. The diagram of the cyclical battle between chaos and order finds a productive format in modern media, ensuring that the myth’s legacy endures in the collective consciousness. The myth’s cultural impact is substantial, revealing its power to traverse time and inform creative expression.
Conclusion: The Legacy of Set and Horus
The enduring legacy of Set and Horus within Egyptian mythology offers profound insights into the complexity of their relationship, which serves as a metaphor for various aspects of human nature. Set, often depicted as the embodiment of chaos and disorder, stands in stark contrast to Horus, who symbolizes order, justice, and kingship. This duality reflects the broader human experience, where opposing forces coexist, influencing both individual character and societal values.
The myth of the ‘bloody eye,’ central to their narrative, is not merely a tale of rivalry and vengeance; rather, it encapsulates themes of conflict, transformation, and reconciliation. The eye, which is often interpreted as a symbol of perception and insight, alludes to the importance of understanding one’s inner struggles and the necessity of confronting them to attain maturity and balance. Through their stories, Set and Horus illuminate the complexities of loyalty, betrayal, and the continual pursuit of equilibrium within the self.
As the dynamics between these two deities unfold throughout history, they impart essential lessons on the dual aspects of existence. The conflict between Set and Horus, while rooted in myth, resonates with the universal human condition, emphasizing the significance of embracing our inner contradictions. Thus, the legacy of these figures transcends ancient texts, encouraging reflection on how individuals navigate their personal battles and societal roles. Their relationship serves as a reminder that light and darkness are inextricably linked, and that understanding this interplay can lead to deeper self-awareness and harmony within the human experience.

Further Reading and Resources
For those intrigued by the rich tapestry of Egyptian mythology, especially the complex narratives surrounding Set and Horus, there exists a wealth of resources that can deepen understanding and appreciation. The following books and articles explore various perspectives, revealing the intricate symbolism and cultural significance tied to the myth of the ‘bloody eye.’
One highly recommended text is “The Complete Gods and Goddesses of Ancient Egypt” by Richard H. Wilkinson. This comprehensive guide delves into the various deities of the Egyptian pantheon, offering insights into their characteristics and relationships, including the antagonistic dynamic between Set and Horus. The author’s approach provides an engaging overview of how these gods influenced ancient Egyptian society and religious practices.
Another noteworthy resource is “Egyptian Myth: A Very Short Introduction” by Geraldine Pinch. This concise yet informative book breaks down key myths, including the story of the ‘bloody eye,’ making it accessible to those who may be new to the subject. The work serves as a useful primer, placing the narratives within the broader context of Egyptian cosmology and culture.
For a more scholarly perspective, consider the article “The Eye of Horus: A Symbol of Protection and Healing” available through the Journal of Egyptian History. It examines the different interpretations of the eye symbol, including its connections to healing and protection. This source is particularly useful for those interested in how the ‘bloody eye’ myth fits into the larger symbolic framework of Egyptian mythology.
Lastly, online resources such as the British Museum’s extensive database provide articles and images related to Egyptian artifacts depicting Set and Horus. This can enhance one’s understanding of how these figures were visually represented and their significance in ancient society. By engaging with these curated texts and articles, readers can expand their knowledge and appreciation of this fascinating mythological landscape.
Indoor Stickers
Art and Artists
Art and Artists
Eye of Horus Unisex Sweatshirt – Ancient Symbol, Modern Comfort
Art and Artists
Eye of Horus Unisex V-Neck T-Shirt – Ancient Symbol, Modern Edge

















